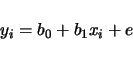 |
(3.2) |
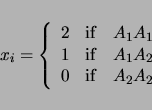
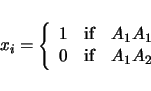
LRmapqtl can also take into account categorical traits, that is other variables such as sex or brood, in its analysis. If your data set contains such information, then there should be a list of the names of these other variables near the beginning of the ``Rcross.out'' formatted file. These names might look as follows:
-Names of the other traits...
1 Sex
2 Line
If you would like to include ``Sex'' and ``Sex by Marker interaction'' terms in your analysis,
then you need to indicate as much to LRmapqtl. If you prefix the name of
one of these variables with a plus sign
-Names of the other traits...
1 +Sex
2 Line
In LRmapqtl, this would consider both Sex and Sex by Marker interaction
terms. In Zmapqtl and SRmapqtl, the Sex by Marker term wouldn't be incorporated, but
the Sex factor would. All other variables that have no + sign at the beginning of their names
will be ignored in the analysis. For the above example, a pair of models will be considered:
| (3.3) | |||
| (3.4) |
Table 3.2 shows the command line options specific to LRmapqtl. As with Qstats, there are few parameters to change. The -t option allows you to specify a trait to analyze. It is trait 1 by default. If you only have one trait, you can ignore this option. If your data set has more than one trait, you can analyze a specific trait by using -t with an integer from 1 to the number of traits. If you want LRmapqtl to analyze all traits, use a value greater than the number of traits.