Meloidogyne hapla
Meloidogyne hapla gbrowse server
Published M. hapla genome sequence fasta file
Updated structural annotation referenced in Guo, et al. 2014. Worm 3:e29158. doi: 10.4161/worm.29158:
Meloidogyne hapla gff-formatted file HapPep5
Augmented Medicago-MhaplaVW9-MhaplaLM reference genome sequence and gff file used for cross-species eQTL mapping:
de novo assembled M. hapla LM genome sequence
The root knot nematode M. hapla is an obligate, biotrophic pathogen of a wide range of hosts. Infective second stage juveniles (J2) enter the root near the root tip and move to the vascular cylinder. There they form a feeding site characterized by modified host cells (giant cells) that serve as a source of nutrients for the nematode.
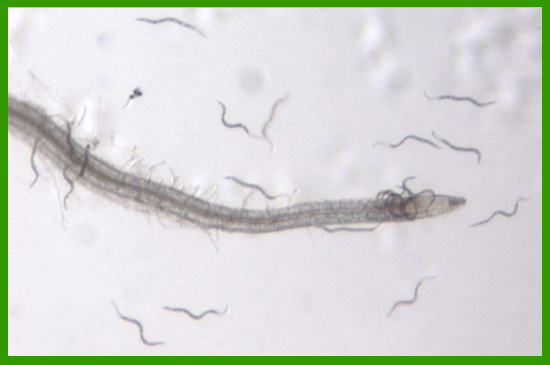
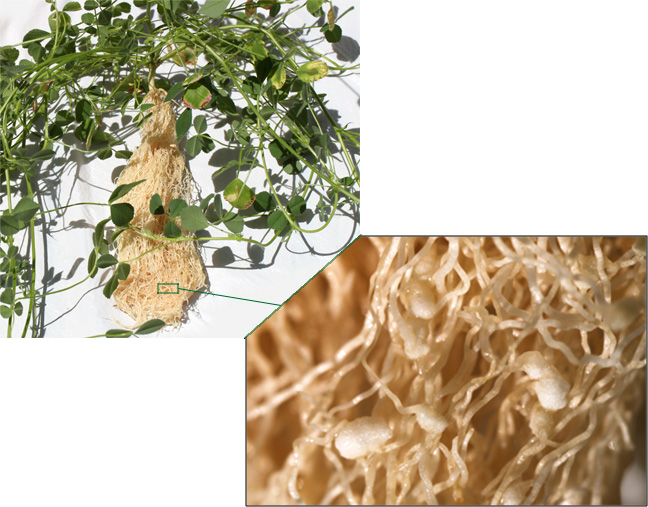
Cortical cells surrounding the giant cells become hypertrophied forming a characteristic gall or root-knot.

The nematode becomes immobile and develops over about a month into an adult female, which lays eggs in a gelatinous mass at the root surface.